Specialities
- Home | Dr. Saneya Pandrowala
Bile Duct Cancer
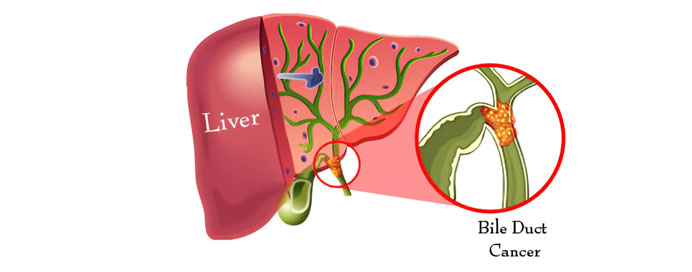
Bile duct cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare but serious cancer that originates in the bile ducts, the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the small intestine to aid in digestion. This cancer is often slow-growing but difficult to detect early because symptoms may be subtle or nonspecific. Common signs include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, pale stools, abdominal pain, itching, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. Risk factors include chronic bile duct inflammation, bile duct cysts, liver diseases such as cirrhosis, infections like liver flukes, and certain genetic conditions. Treatment depends on the location and stage of the cancer and may involve surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination. Early detection improves outcomes, but prognosis is generally poor for advanced disease due to the cancer’s tendency to spread to nearby organs and lymph nodes.
- Location: Bile ducts (intrahepatic, perihilar, or distal).
- Symptoms: Jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, abdominal pain, itching, fatigue, weight loss.
- Risk Factors: Chronic bile duct inflammation, bile duct cysts, liver cirrhosis, liver fluke infections, genetic predisposition.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests (liver function tests, tumor markers like CA 19-9), imaging (ultrasound, CT, MRI, MRCP), biopsy.
- Treatment: Surgery (resection or liver transplant in select cases), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy in advanced cases.
- Prognosis: Better if detected early; generally poor in advanced or unresectable cases.
